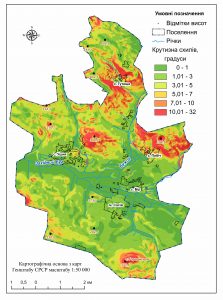
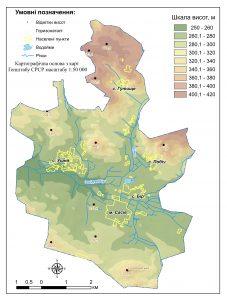
Geoinformation modeling – is a high-tech process of creating a terrain model of certain territory in the environment of geographic information systems. The created model visualizes the quantitative and qualitative parameters of the simulated area, presents the intensity of the processes (for example, geomorphological, hydrological, technological), gives an objective assessment of the state of the object (urban environment, individual components of the natural environment, human economic activity). Typically, GIS modeling is a decision-making tool in the development of recommendations for optimizing environmental management, urban planning, reducing the destructive anthropogenic environmental impacts, preventing the occurrence of man-made incidents and the development of dangerous phenomena and processes.
Get the opportunity to understand complex structures, manifest and justify spatial processes and patterns that are important for your business, using data from cartography and GIS modeling. Use geoinformation modeling to display spatial data, visualize information and knowledge.